Google Ranking Factors for Law Firms: What Impacts SEO the Most?

Josh Brown
CEO & Founder, Josh Brown Consulting

SEO For Lawyers Guide
Google ranking factors for law firms are signals used to determine how well a law firm’s website appears in search results, especially for legal services and location-based queries. Improving Google search ranking involves optimizing content quality, speeding up page load time, gaining high-quality backlinks, and enhancing user experience. These align with Google’s core evaluation system, known as E-E-A-T—Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trust.
Legal websites fall under YMYL (Your Money or Your Life), a category where Google enforces stricter standards for accuracy and trust. This means legal content must be factually correct, well-sourced, and authored by qualified professionals. Google uses over 200 ranking signals, including content relevance, mobile usability, semantic context, backlink quality, and technical performance.
Key quality signals include E-E-A-T, content freshness, page speed, mobile-friendliness, structured data, and Core Web Vitals. For new law firm websites, SEO ranking starts with indexing via Google Search Console, publishing consistent high-value content, building internal links, and acquiring backlinks, while avoiding keyword stuffing or low-quality practices.
Local ranking factors include the firm’s proximity to the searcher, Google Business Profile optimization, local citations, reviews, and keyword relevance. While domain names don’t directly affect SEO, exact-match or branded domains boost user trust or CTR. HTTPS is a confirmed ranking factor, offering security and user trust, though it carries less weight than strong content or backlinks.
Listed below are 30 Google Ranking Factors for Law Firms.
1. Backlinks (quality and quantity)
2. Content quality and relevance
3. Google Business Profile optimization
4. Reviews and online reputation (especially Google reviews)
5. Site speed and Core Web Vitals
6. Mobile-friendliness
7. On-page optimization (title tags, H1S, keyword usage)
8. Local citations (NAP consistency)
9. Domain authority and age
10. Behavioral signals (click-through rate, bounce rate, dwell time)
11. Schema markup / structured data
12. Internal linking structure
13. Geographic keyword targeting
14. HTTPS (secure website)
15. Technical SEO (crawlability, indexation, site structure)
16. Content freshness and updates
17. User experience (UX)
18. Page depth (important content not buried too deep)
19. Use of multimedia (images, video)
20. Social signals (indirect but cited)
21. Practice area landing pages
22. Localized content (specific city/neighborhood targeting)
23. Image optimization (alt text, file names)
24. Outbound links to authoritative sources
25. Sitemap optimization
26. Canonical URLs and duplicate content management
27. Click-to-call functionality (mobile)
28. Blog presence and activity
29. Domain keyword inclusion (e.g., “criminaldefenselosangeles.com”)
30. Proximity to searcher (for local SEO)
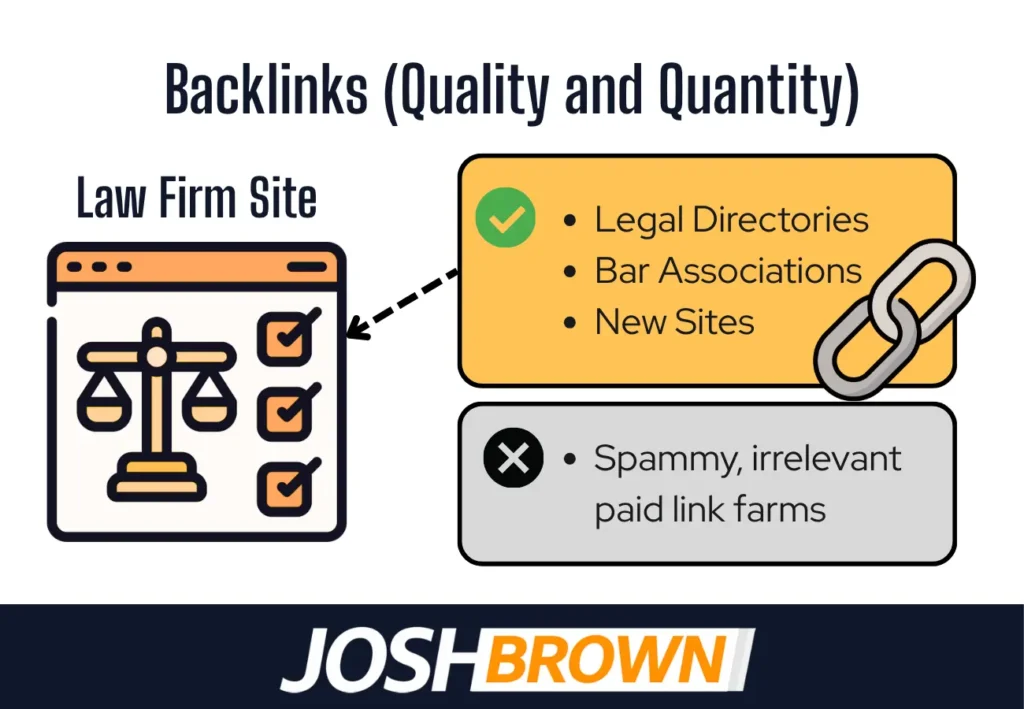
1. Backlinks (quality and quantity)
Backlinks are links from external websites pointing to a law firm’s site. In Law Firm SEO, they act as trust and authority signals. High-quality backlinks from legal directories, bar associations, and news sites improve domain authority and search visibility. Low-quality links reduce trust and trigger penalties.
Backlinks affect organic and local rankings by signaling authority and relevance. Google favors links from authoritative, topic-relevant sites. Quality links placed contextually carry more weight than random or spammy links.

2. Content Quality and Relevance
Content quality and relevance refer to how well a law firm’s website answers user queries with accurate, useful, and legally sound information. In Law Firm SEO, content must directly match search intent, use clear legal explanations, and reflect professional authority. Thin, duplicate, or irrelevant content lowers engagement and visibility.
Google ranks legal content using E-E-A-T, with added scrutiny for YMYL topics. Accurate, updated, and well-structured content earns higher placement and longer user dwell time. Relevance ensures alignment between page content and keyword targets.
Law firms must write in plain language, match content to legal search terms, and cover client-relevant questions. Include FAQs, case examples, and local law references. Keep content updated and avoid keyword stuffing to improve local pack visibility and organic performance.
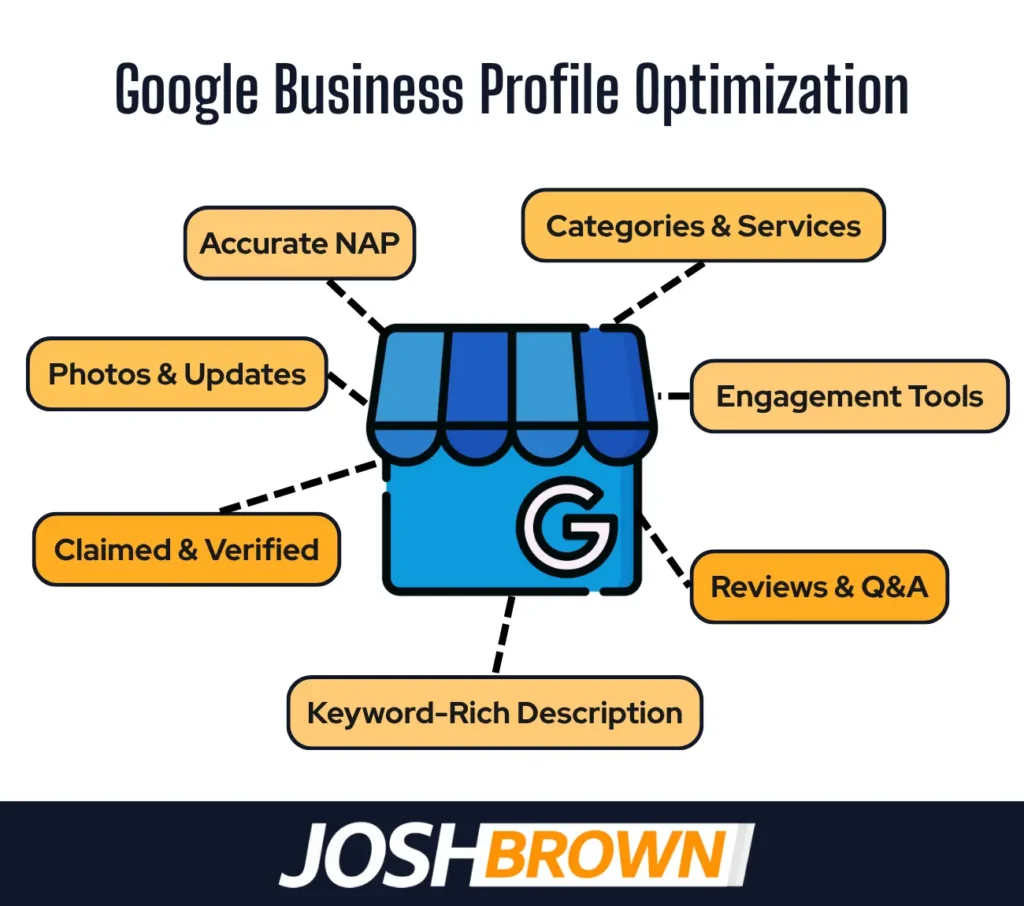
3. Google Business Profile Optimization
Google Business Profile optimization involves setting up and maintaining a law firm’s profile to appear in local search and map results. It directly impacts visibility in the Local Pack, where most local clients find legal services. An incomplete or unverified profile limits reach.
Google uses profile data, like business name, address, phone, hours, services, and categories, as ranking signals for local queries. Profiles with accurate info, relevant keywords, and frequent updates perform better. Client interactions like reviews and Q&A also influence trust and ranking.
Law firms must claim and verify their profile, choose the right categories, write a keyword-targeted business description, upload location-specific photos, and regularly update services. Activate messaging, respond to reviews, and post firm updates to improve local search ranking and client engagement.

4. Reviews and Online Reputation (Especially Google Reviews)
Reviews and online reputation reflect public feedback about a law firm’s service quality, professionalism, and results, especially through Google reviews. In Law Firm SEO, positive reviews increase trust and influence local ranking, while negative reviews signal risk to both users and Google.
Google prioritizes businesses with high ratings, review volume, and consistent responses. Verified reviews containing keywords, service references, and location details improve local visibility and user trust. Reputation also affects click-through rates and engagement.
Law firms must ask satisfied clients to leave reviews, especially on Google, and respond professionally to all feedback. Maintain consistent review generation, monitor third-party platforms, and handle complaints transparently to strengthen local pack performance and drive organic traffic.

5. Site Speed and Core Web Vitals
Site speed and Core Web Vitals measure how quickly and smoothly a law firm’s website loads and responds to user interaction. Google uses these metrics to assess technical performance and rank pages that deliver better experiences, especially on mobile.
Core Web Vitals include Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Poor performance reduces rankings, increases bounce rates, and limits visibility in both organic results and the Local Pack.
Law firms must optimize image sizes, reduce server response times, enable caching, and minimize code bloat. Use Google Page Speed Insights or Search Console to monitor scores. Fast, stable pages improve website optimization, user satisfaction, and search visibility.

6. Mobile-Friendliness
Mobile-friendliness refers to how well a law firm’s website functions on smartphones and tablets. Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning mobile performance directly impacts search rankings.
A mobile-friendly site adjusts layout, text, and navigation for smaller screens. Poor usability, like overlapping elements or hard-to-click buttons, hurts engagement and ranking. Most legal searches now happen on mobile, making mobile optimization critical for local search ranking and organic traffic.
Law firms must use responsive design, readable fonts, fast-loading elements, and clear calls-to-action on mobile. Test using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Tool. A mobile-optimized site improves user experience, lowers bounce rates, and ranks higher in both local and national search results.
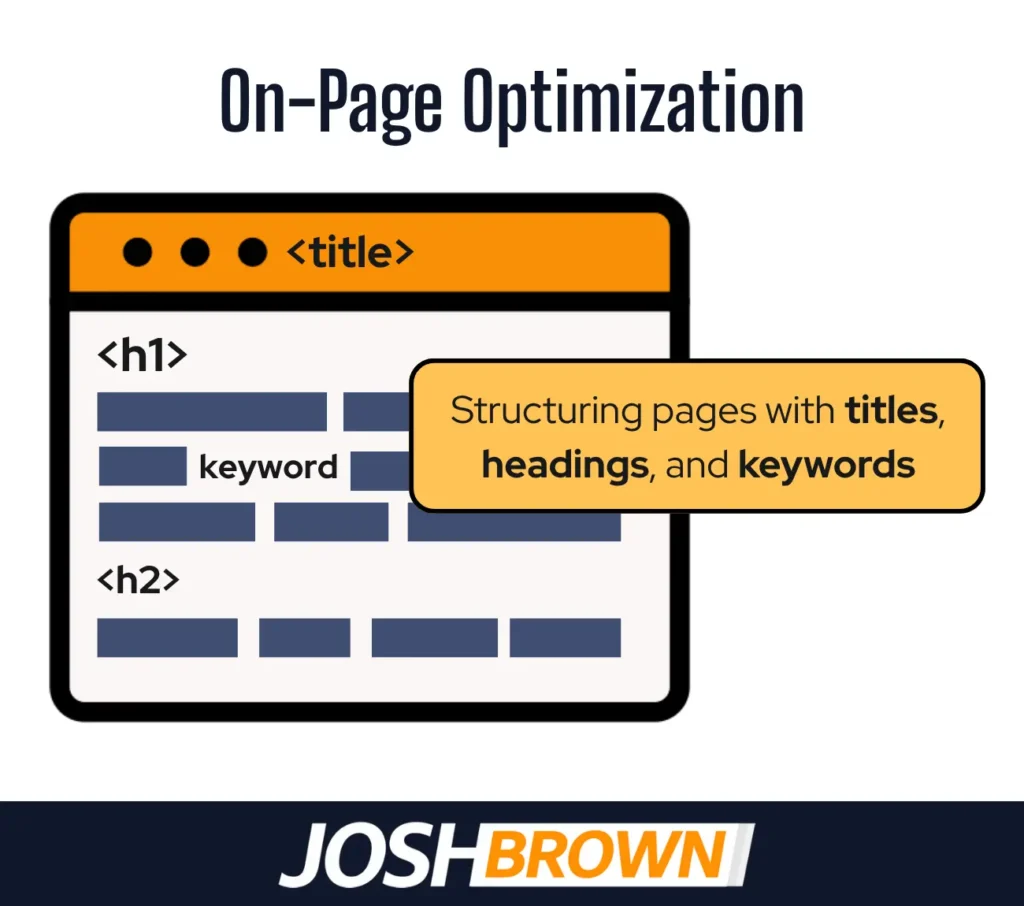
7. On-Page Optimization (Title Tags, H1s, Keyword Usage)
On-page optimization involves structuring a law firm’s web pages with clear titles, headings, and keyword placement to signal relevance to search engines. It helps Google understand content focus and match pages with user queries.
Key elements include unique title tags, descriptive H1 headings, and natural keyword usage in content, URLs, and image alt text. Overuse or stuffing reduces ranking and triggers penalties. Structured on-page signals boost content relevance and crawl efficiency.
Law firms must include target legal keywords and location modifiers in titles and headings. Use one H1 per page, write concise meta descriptions, and ensure internal consistency between keywords and page topics. Clean on-page structure improves legal marketing visibility and strengthens website optimization.
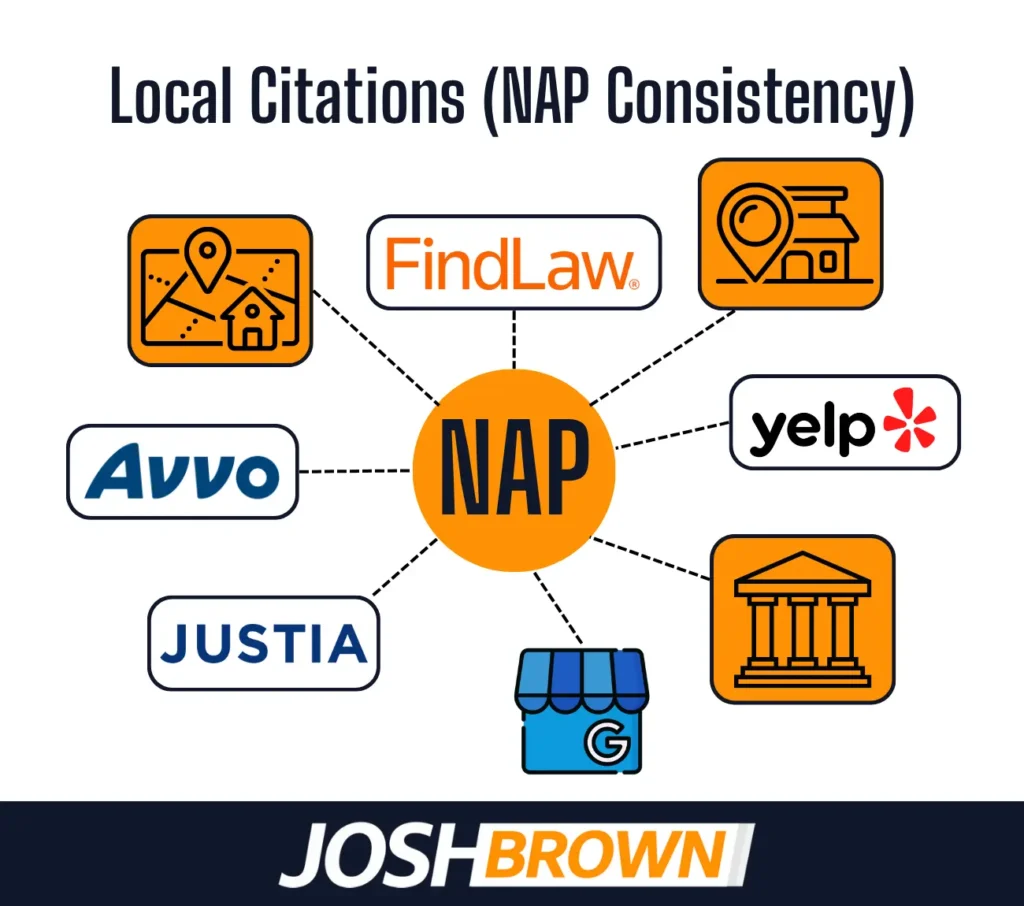
8. Local Citations (NAP Consistency)
Local citations are mentions of a law firm’s Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) across online directories and business listings. These citations validate a firm’s location and presence, strengthening trust and improving local search ranking.
Google uses consistent NAP data to verify business legitimacy and reinforce proximity-based results in the Local Pack. Inconsistent or duplicate listings confuse algorithms and weaken local visibility.
Law firms must ensure identical NAP details across major directories like Yelp, Avvo, Justia, and legal-specific platforms. Use a citation management tool to monitor, update, and suppress duplicates. NAP consistency boosts Google Business Profile accuracy and reinforces geographic relevance.

9. Domain Authority and Age
Domain authority and age refer to the trustworthiness and longevity of a law firm’s website as evaluated by search engines. Older domains with consistent content and clean link profiles tend to rank higher due to established credibility.
While domain authority is not a direct Google ranking factor, it reflects backlink strength, content quality, and overall SEO performance. New domains face a longer ramp-up period for ranking, especially in competitive legal markets.
Law firms must build authority over time by earning high-quality backlinks, publishing trustworthy content, and avoiding spammy tactics. Use SEO tools to monitor domain metrics and focus on long-term website optimization to support sustainable growth in organic traffic and local search ranking.
10. Behavioral Signals (Click-Through Rate, Bounce Rate, Dwell Time)
Behavioral signals track how users interact with a law firm’s website in search results and on the page. These include click-through rate (CTR), bounce rate, and dwell time, metrics that reflect user satisfaction and content relevance.
Google uses these engagement patterns to refine rankings. A high CTR suggests a strong title and meta description appeal. Low bounce rates and longer dwell times signal that visitors find the content useful and stay to explore.
Law firms must write compelling meta titles, match content to user intent, and structure pages for easy reading. Use clear calls-to-action, fast loading speeds, and mobile optimization to reduce drop-offs. Strong engagement improves local pack visibility and boosts overall law firm SEO performance.
11. Schema Markup / Structured Data
Schema markup is a type of structured data added to a law firm’s website code to help search engines better understand page content. It enhances how listings appear in search results by enabling rich snippets like reviews, FAQs, and business details.
Google uses structured data to improve content indexing and display additional details directly in SERPs. For law firms, schema attorney names, practice areas, office hours, and client ratings boost visibility and click-through rate.
Law firms must implement LocalBusiness, LegalService, and Review schema types. Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to verify accuracy. Correct markup improves legal marketing presence in search results and supports website optimization for better organic traffic.
12. Internal Linking Structure
Internal linking structure refers to how pages on a law firm’s website are connected through hyperlinks. These links guide users and search engines through site content, distribute page authority, and support contextual relevance.
Google uses internal links to crawl pages, understand hierarchy, and evaluate the importance of individual URLs. Clear linking improves SEO by helping high-authority pages boost visibility for deeper, related content.
Law firms must connect practice area pages to related blog posts, FAQs, and service areas using keyword-rich anchor text. Avoid orphaned pages and broken links. A strong internal structure improves website optimization, boosts organic traffic, and keeps visitors engaged longer.
13. Geographic Keyword Targeting
Geographic keyword targeting involves using location-specific terms within a law firm’s content to align with local search intent. These keywords help Google connect legal services to users searching in a specific city, neighborhood, or region.
Google favors pages that match both service and location queries in local and organic results. Terms like “divorce lawyer in Houston” or “Los Angeles criminal defense attorney” increase relevance for local search ranking.
Law firms must include city or region names in page titles, H1s, meta descriptions, URLs, and body text. Create separate landing pages for different locations served. Consistent geographic targeting boosts visibility in the Local Pack and strengthens law firm SEO.

14. HTTPS (Secure Website)
HTTPS is the secure version of HTTP, encrypting data between a law firm’s website and its users. Google confirmed HTTPS as a ranking factor to promote safe browsing and data protection, especially for sensitive services like legal consultations.
While HTTPS is a lightweight ranking signal, it contributes to trust, lowers bounce rates, and is a prerequisite for other SEO tools and features. Users are more likely to stay on secure sites, which improves engagement.
Law firms must install an SSL certificate and ensure all site URLs redirect to the HTTPS version. Avoid mixed content errors. A secure site enhances website optimization, supports Google Business Profile credibility, and meets basic law firm SEO standards.
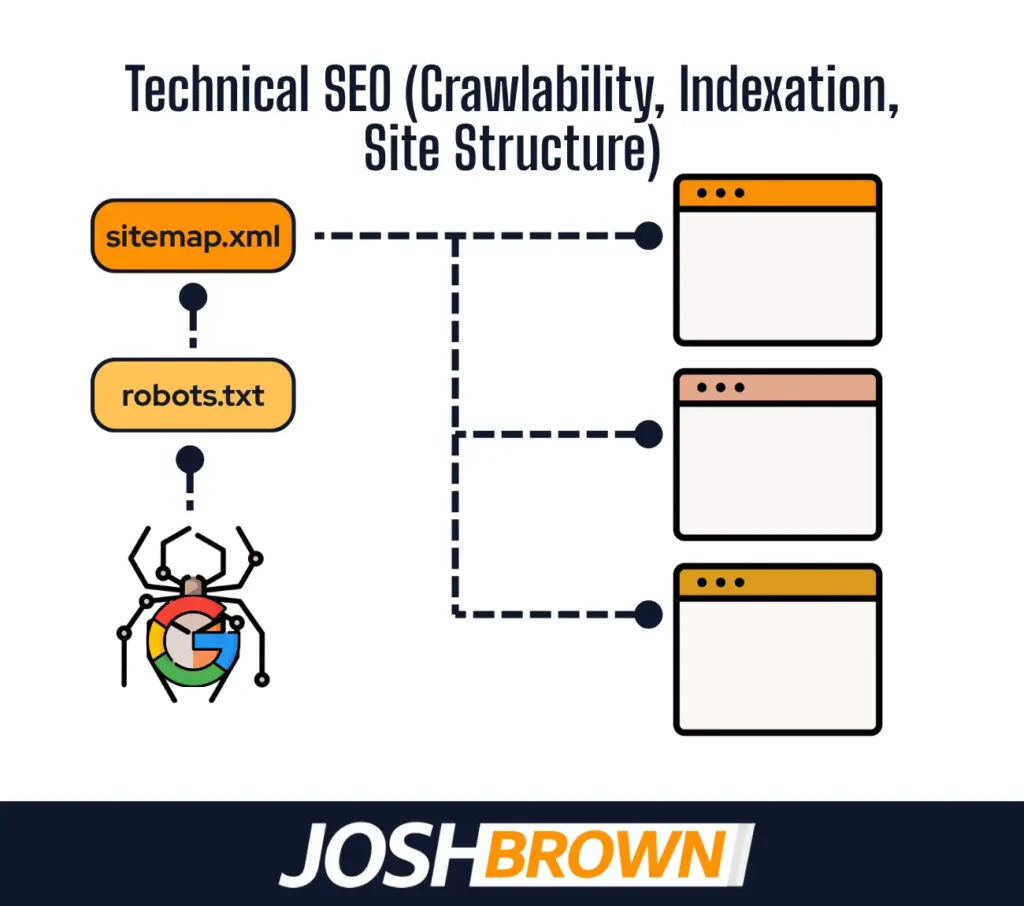
15. Technical SEO (Crawlability, Indexation, Site Structure)
Technical SEO is the backend setup that ensures a law firm’s website is crawlable, indexable, and logically structured for search engines. It affects how well Google accesses and ranks the site’s content.
Core elements include clean URL structure, XML sitemaps, robots.txt configuration, canonical tags, and structured navigation. Errors in these areas block indexing or cause duplicate content issues, reducing visibility.
Law firms must audit their site using tools like Google Search Console and fix crawl errors, broken links, and redirect loops. Use flat architecture, prioritize mobile usability, and keep URLs short and descriptive. Strong technical SEO supports organic traffic and ensures consistent local search ranking performance.

16. Content Freshness and Updates
Content freshness refers to how recently a law firm’s website content was published or updated. Google favors updated content for queries where accuracy and timeliness matter, especially in legal topics affected by law changes or court rulings.
Fresh content signals ongoing relevance and boosts engagement, while outdated pages lose rankings. Regular updates improve trust signals under Google’s E-E-A-T framework, particularly for YMYL pages.
Law firms must review and update key practice pages, blogs, and FAQs regularly. Add recent legal developments, case examples, or changes in statutes. Frequent updates improve law firm SEO consistency and help maintain organic traffic in competitive search results.
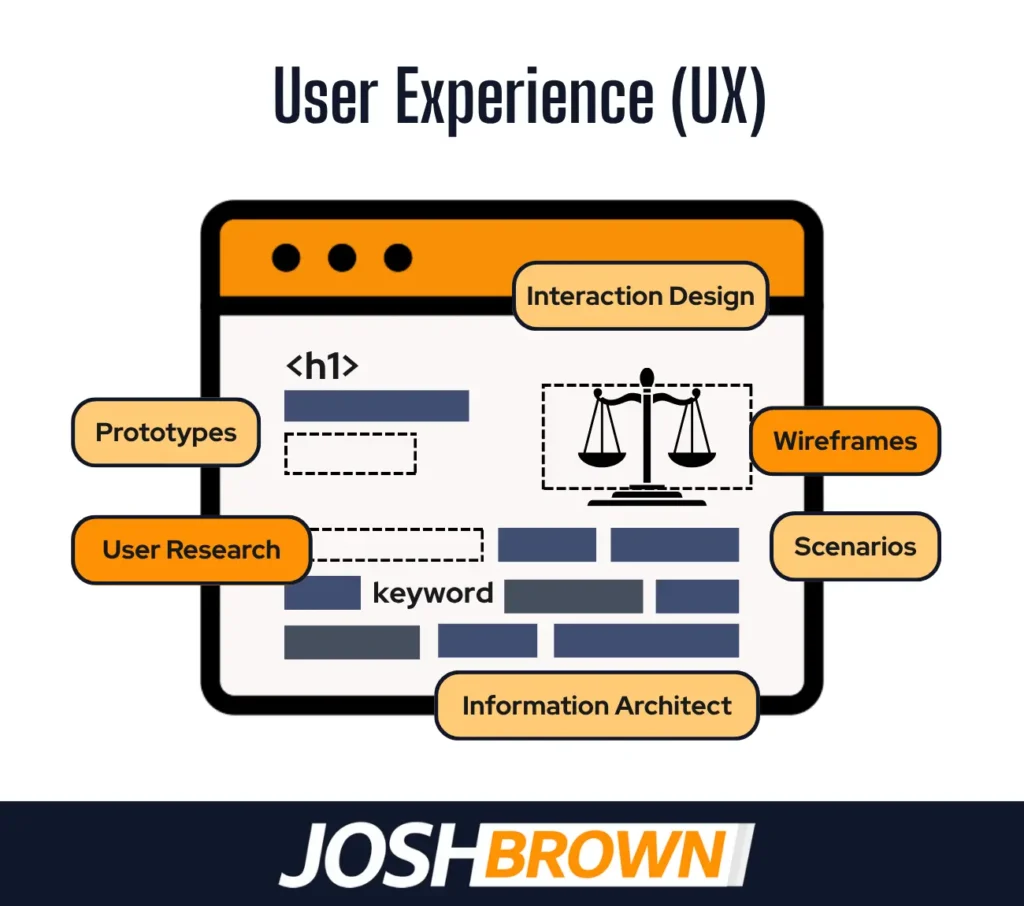
17. User Experience (UX)
User experience (UX) measures how easily and effectively visitors navigate and interact with a law firm’s website. Google tracks UX signals like bounce rate, page engagement, and task completion to influence rankings.
A poor UX, slow load times, confusing layout, or broken elements reduce time on site and weaken SEO signals. Good UX supports readability, accessibility, and mobile usability, which improves trust and conversions.
Law firms must use clear navigation, fast-loading pages, readable text, and visible calls-to-action. Eliminate pop-up clutter, test usability on all devices, and guide visitors to contact forms or service pages. Strong UX directly supports website optimization and improves organic traffic retention.
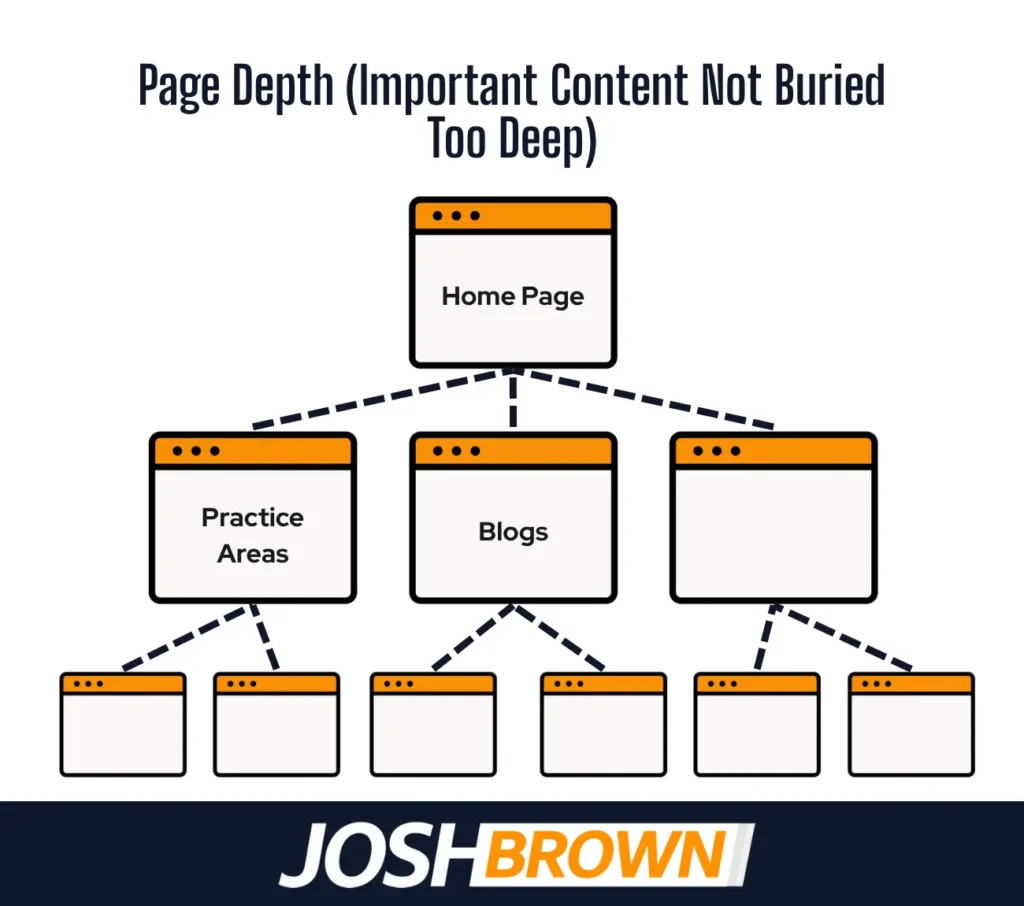
18. Page Depth (Important Content Not Buried Too Deep)
Page depth refers to how many clicks it takes to reach important content from a law firm’s homepage. Shallow page depth makes high-value pages easier for users and search engines to access and rank.
Google prioritizes content that’s accessible within three clicks or fewer. Deeply buried pages are crawled less, reducing visibility and weakening internal link equity.
Law firms must place key pages, like practice areas, attorney profiles, and contact forms, close to the homepage. Use strategic internal linking, simple navigation menus, and flat site architecture. Optimized page depth improves crawlability, boosts law firm SEO, and strengthens local search ranking.

19. Use of Multimedia (Images, Video)
Use of multimedia refers to integrating images, videos, infographics, and visual aids into a law firm’s website content. Multimedia enhances comprehension, increases engagement, and improves how users interact with legal information.
Google favors pages that hold user attention and reduce bounce rates. Videos explaining legal processes or images showing office locations help retain visitors and support E-E-A-T signals, especially for complex legal topics.
Law firms must embed short videos, use original images with descriptive filenames, and include captions or transcripts. Optimize media for fast loading and mobile compatibility. Strong multimedia use improves user experience, extends dwell time, and supports higher organic traffic.

20. Social Signals (Indirect but Cited)
Social signals refer to likes, shares, comments, and mentions of a law firm’s content across platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter. While not direct ranking factors, they indicate engagement and brand awareness, which influence content visibility.
High-performing content on social media can attract backlinks, increase traffic, and improve search performance indirectly. Google uses these behavioral patterns to assess authority and relevance, especially for newer law firm websites.
Law firms must actively share blog posts, case results, and FAQs on professional social platforms. Encourage sharing, monitor engagement, and maintain consistent branding. Strong social activity supports broader legal marketing reach and contributes to improved organic traffic over time.

21. Practice Area Landing Pages
Practice area landing pages are dedicated pages focused on specific legal services a law firm offers, such as personal injury, criminal defense, or family law. These pages help target precise search queries and improve content relevance for both users and search engines.
Google ranks specialized pages higher for service-specific searches, especially when they include geographic terms and answer user intent clearly. They also support internal linking and keyword targeting across the site.
Law firms must create individual, keyword-rich pages for each practice area with localized content, FAQs, and strong calls-to-action. Include schema markup, optimize titles and meta descriptions, and link to related blog posts. Well-structured landing pages improve local search ranking and increase organic traffic from high-conversion queries.
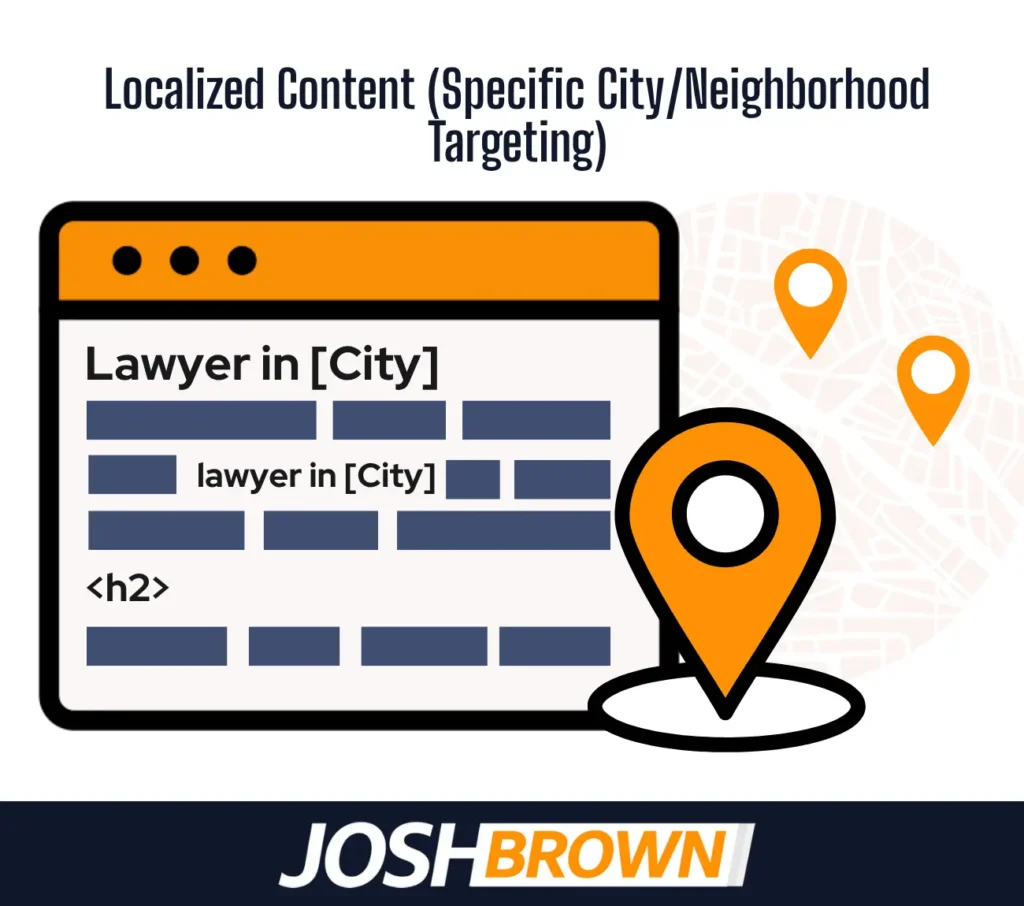
22. Localized Content (Specific City/Neighborhood Targeting)
Localized content refers to web pages and blog posts tailored to specific cities, neighborhoods, or regions served by a law firm. It helps law firms appear in geo-targeted search queries and improves relevance for local users.
Google favors location-specific pages that match user intent, especially in legal searches involving proximity or jurisdiction. Pages that reference neighborhoods, courts, or local laws rank better in the Local Pack and regional results.
Law firms must create separate pages for each target city or service area, including local keywords, maps, and contact details. Add location-specific case results or client reviews to strengthen local relevance. Consistent localized content supports stronger local search ranking and drives qualified organic traffic.

23. Image Optimization (Alt Text, File Names)
Image optimization involves formatting and labeling images so they load quickly and contribute to a law firm’s SEO performance. Google reads image metadata to understand content context and improve search relevance, especially in image-based search results.
Alt text and descriptive file names help with accessibility, indexing, and keyword relevance. Large or uncompressed images slow site speed and hurt rankings through Core Web Vitals signals.
Law firms must use descriptive, keyword-rich file names (e.g., “houston-personal-injury-lawyer.jpg”), include concise alt text, and compress files without quality loss. Serve images in next-gen formats (WebP) and enable lazy loading. Optimized images improve site speed, support website optimization, and reinforce law firm SEO content context.
24. Outbound Links to Authoritative Sources
Outbound links are hyperlinks from a law firm’s website to reputable external sources such as legal publications, government sites, or court databases. These links help validate content and demonstrate that the firm references trustworthy information.
Google uses outbound linking as a quality indicator, especially for YMYL content like legal advice. Linking to credible sources supports E-E-A-T and signals transparency, improving content reliability and SEO performance.
Law firms must link to official legal sources (e.g., statutes, court rulings, bar associations) where relevant. Use natural anchor text, avoid excessive outbound links, and open them in new tabs to preserve session time. Strategic outbound linking strengthens content credibility and supports organic traffic growth.
25. Sitemap Optimization
Sitemap optimization involves creating and maintaining an XML sitemap that lists all important pages on a law firm’s website for search engine indexing. It guides crawlers to discover, understand, and prioritize content during indexing.
Google uses sitemaps to efficiently crawl websites, especially those with complex structures or new content. A clear, updated sitemap improves coverage, reduces crawl errors, and supports fast indexation of new or updated legal pages.
Law firms must submit their sitemap through Google Search Console, ensure it includes all indexable URLs, and exclude duplicate or redirecting pages. Update the sitemap after publishing new content and monitor crawl stats. A clean sitemap boosts technical SEO and improves law firm SEO visibility in search results.
26. Canonical URLs and Duplicate Content Management
Canonical URLs are tags that tell search engines which version of a page is the primary one when similar or duplicate content exists on a law firm’s site. This prevents indexing issues and consolidates ranking signals.
Google penalizes duplicate content by diluting page authority and confusing crawl priority. Canonical tags ensure the correct page is indexed and ranked, preserving SEO equity.
Law firms must use canonical tags on similar service pages, avoid URL variations with identical content, and audit for unintentional duplication. Tools like Google Search Console and Screaming Frog help detect and fix issues. Proper canonicalization improves technical SEO and protects organic traffic from split ranking.

27. Click-to-Call Functionality (Mobile)
Click-to-call functionality allows mobile users to tap a phone number on a law firm’s website and instantly place a call. It simplifies user interaction and increases lead conversion from mobile search traffic.
Google prioritizes mobile usability, and click-to-call improves engagement metrics like time-on-site and conversion rate. For local searches, especially in urgent legal cases, fast contact options influence both user behavior and local search ranking.
Law firms must use HTML click-to-call tags (tel:), display numbers prominently on mobile pages, and verify that buttons are easy to tap. Track call clicks through analytics to measure performance. Enabling click-to-call supports website optimization and increases mobile-driven organic traffic.

28. Blog Presence and Activity
Blog presence and activity refer to how consistently a law firm publishes informative, relevant articles that address legal topics, client questions, or recent developments. Active blogs demonstrate subject-matter authority and support long-term SEO growth.
Google values fresh, topical content that aligns with user search intent. Regular blogging improves indexing frequency, supports internal linking, and builds keyword relevance across multiple search queries.
Law firms must publish posts that target client pain points, explain legal processes, or respond to current legal news. Maintain a consistent posting schedule, optimize posts with headings and keywords, and link to core service pages. An active blog supports law firm SEO, improves content freshness, and drives sustained organic traffic.

29. Domain Keyword Inclusion (e.g., “criminaldefenselosangeles.com”)
Domain keyword inclusion involves using legal service terms or geographic identifiers in a law firm’s domain name. While not a direct Google ranking factor, it improves perceived relevance and increases click-through rates.
Google’s algorithms now rely more on content quality and contextual signals than on exact-match domains. However, keyword-rich domains influence user trust and search behavior when matched with clear branding.
Law firms use service-location combinations (e.g., “houstonduilawyer.com”) for marketing clarity but must focus on strong content and branding. Avoid spammy or overly long domains. Effective use of domain keywords supports legal marketing and aids organic traffic through better visibility and recall.
30. Proximity to Searcher (for Local SEO)
Proximity to the searcher measures how physically close a law firm’s office location is to the person performing a local search. It is one of the most influential factors in Google’s local search ranking algorithm.
Google prioritizes businesses that are geographically nearest to the searcher, especially for service-related queries with location intent. Even with strong SEO, distant firms rank lower in local results.
Law firms must ensure accurate address information on their Google Business Profile, local citations, and website. Open additional verified locations if serving multiple cities. Proximity, combined with relevance and prominence, improves visibility in the Local Pack and drives qualified organic traffic from nearby users.
How can I increase my Google search ranking?
You can increase your Google search ranking by improving technical performance, creating useful content, and building authority through external signals.
Listed below are practical strategies to boost search ranking and improve Google SEO performance.
- Improve page speed and Core Web Vitals: Optimize loading time, mobile responsiveness, and visual stability for a better user experience.
- Use keywords naturally in headings, content, and metadata: Match search intent without overstuffing or duplicating terms.
- Earn high-quality backlinks from trusted sites: Build authority through legal directories, guest posts, and digital PR.
- Create useful, updated content for every legal service: Target client questions, use structured layouts, and update regularly.
- Optimize your Google Business Profile: Add accurate contact info, business hours, reviews, and legal service categories.
- Structure internal links to reinforce page relevance: Connect blog posts, service pages, and FAQs with descriptive anchor text.
- Use schema markup for legal services, reviews, and business details: Help search engines understand your content structure.
- Maintain consistent NAP citations across all directories: Boost local trust and support Google search ranking via Josh Brown’s SEO for Lawyers strategies.
What does YMYL mean in SEO, and why does it matter?
YMYL in SEO matters because it refers to content that can impact a person’s finances, health, or safety, requiring stricter quality standards from Google. YMYL stands for “Your Money or Your Life,” and includes pages related to law, medical advice, financial planning, and personal security. Google holds these pages to higher scrutiny because low-quality or misleading content in these areas causes real-world harm.
To rank well, YMYL content must demonstrate strong E-E-A-T—Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trust. Law firm websites fall under YMYL, meaning their content must be accurate, professionally written, and factually reliable. Poor-quality YMYL content faces lower rankings or deindexing, making SEO content quality and source credibility critical for visibility and trust.
How does Google rank websites?
Google ranks websites by analyzing hundreds of signals that measure relevance, content quality, technical performance, and user experience. The Google ranking algorithm evaluates how well a page matches a search query, prioritizing those with helpful content, proper keyword usage, and strong backlinks.
Mobile-friendliness, page speed, and structured data influence crawlability and visibility. Positive user engagement, like a low bounce rate and longer dwell time, also supports higher SEO ranking. Sites with clear structure, E-E-A-T signals, and secure connections (HTTPS) are more likely to earn top page position in search results.
What quality signals does Google use for ranking?
Google quality signals used for ranking include backlinks, content expertise, page speed, mobile usability, and HTTPS, which help evaluate trust, relevance, and usability.
Listed below are core SEO metrics and Google site evaluation factors.
- Backlinks: Links from authoritative websites that pass trust and improve search visibility.
- Content Expertise (E-E-A-T): Measures the creator’s experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trust.
- Page Speed: Faster load times improve user experience and support Core Web Vitals.
- Mobile Usability: Ensures content displays correctly and functions well on mobile devices.
- HTTPS: Secures user data, increasing site trust and ranking potential.
- Structured Data (Schema Markup): Makes content easier for Google to interpret and display in rich results.
- User Engagement: Signals like bounce rate and dwell time reflect content value and relevance.
- Content Freshness: Updated content ranks better for timely or evolving topics.
- Internal Linking: Improves crawlability and strengthens authority flow between pages.
How can SEO ranking be improved for a new website?
SEO rankings can be improved for a new website by implementing structured steps that build authority, optimize visibility, and align with search engine requirements. Following these steps helps improve small website performance and increases visibility in competitive legal searches.
Listed below are actions to boost search engine ranking and grow domain authority.
- Conduct keyword research for services and location: Target long-tail and local legal keywords with clear intent.
- Implement technical SEO setup: Use HTTPS, submit a sitemap, fix crawl errors, and ensure mobile responsiveness.
- Create high-quality, keyword-aligned content: Build out service pages, blog posts, and FAQs that match search intent.
- Optimize on-page elements: Include keywords in title tags, H1s, meta descriptions, and URLs.
- Use internal links to connect pages: Improve navigation and distribute authority across key legal content.
- Earn backlinks from trusted directories and partners: Build early authority by listing on legal directories and local business sites.
- Track performance and update content: Use analytics to refine SEO strategy and enhance engagement.
What are the ranking factors for local search?
Ranking factors for local search include Google Business Profile optimization, NAP consistency, local citations, proximity to the searcher, and reviews. These signals determine how law firms appear in the Google Maps listing and affect local search ranking performance. A 2023 Whitespark study confirmed that GBP signals, proximity, and reviews dominate local rankings. Use local search tools to monitor and improve these signals.
Listed below are the main local SEO drivers.
- Google Business Profile optimization: Complete profiles with correct business details, services, and categories improve local visibility.
- NAP consistency: Matching Name, Address, and Phone number across directories reinforces location accuracy.
- Local citations: Listings on legal directories and business platforms validate business presence.
- Proximity to the searcher: Closer offices are favored for location-specific queries.
- Online reviews: Volume and quality of Google reviews influence trust and map pack rankings.
- Keyword relevance: Business names and descriptions that match search terms improve result alignment.
- Local backlinks and geographic content: Links and on-site content tied to the service area boost authority.
Does a domain name impact SEO or RankBrain?
Yes, a domain name impacts SEO and RankBrain, but only indirectly through user behavior, branding, and click-through rates, not direct ranking weight. Keyword-rich domains like “houstoninjurylawyer.com” improve user trust and relevance perception, increasing clicks. However, Google’s RankBrain algorithm prioritizes content relevance and search intent over exact-match domains.
While domain SEO value once favored keyword-stuffed URLs, modern algorithms now emphasize contextual quality, topical authority, and user engagement. Branded domains help build recognition and link profiles over time, which influence rankings more than keywords in the URL. Clear, memorable domains with relevant content and structured SEO remain more effective than relying solely on domain phrasing.
Is HTTPS a ranking factor for SEO?
Yes, HTTPS is a ranking factor for SEO and contributes to improved security, user trust, and a slight ranking boost in Google’s algorithm. It plays a vital role in technical SEO, protecting user data and improving trust by preventing browser warnings. As detailed in this technical SEO audit, enabling HTTPS also ensures your site complies with Google’s secure browsing standards.
Although it’s a lightweight signal compared to backlinks or content depth, a 2020 study by Brian Dean found that HTTPS-enabled websites were slightly more likely to rank on the first page. Law firms in particular benefit from HTTPS for both data integrity and credibility. Always implement HTTPS across your entire domain and verify it in Google Search Console to maximize its SEO benefit.
